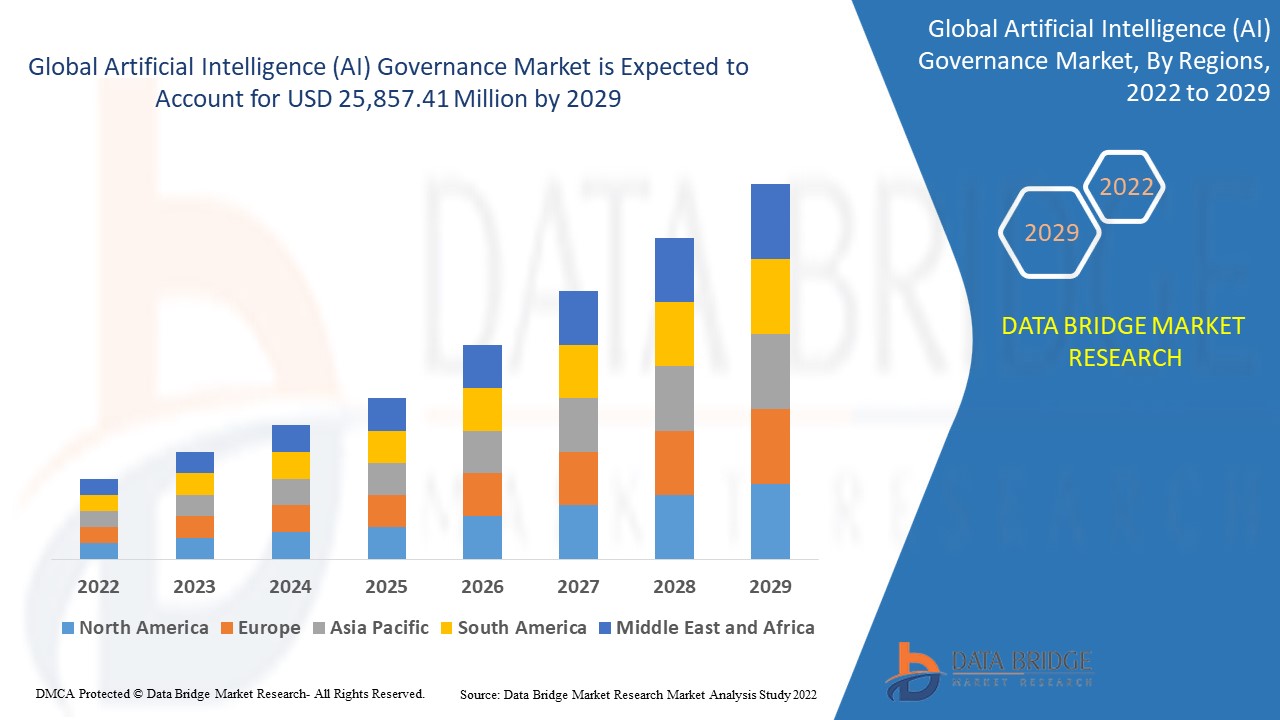
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries and transforming societies. From healthcare and finance to transportation and education, AI technologies are driving innovation and efficiency. However, with great power comes great responsibility. The rise of AI brings forth significant ethical, legal, and social challenges that necessitate robust governance frameworks. AI governance encompasses the policies, procedures, and regulations that ensure the responsible development, deployment, and use of AI technologies. This comprehensive guide explores the landscape of AI governance, covering its importance, key principles, current frameworks, challenges, and future prospects. Whether you are a policymaker, industry leader, or an AI enthusiast, this article provides valuable insights into the crucial domain of AI governance.
What is AI Governance?
Definition and Overview
AI governance refers to the set of rules, practices, and standards designed to guide the ethical and responsible use of AI technologies. It aims to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed in ways that are fair, transparent, accountable, and aligned with societal values and legal requirements.
Key Objectives
- Ethical AI Development: Ensuring that AI technologies are developed in accordance with ethical principles, such as fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to laws and regulations that govern the use of AI in various sectors and jurisdictions.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with AI, including bias, privacy violations, and security threats.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving diverse stakeholders in the governance process to ensure that AI systems address the needs and concerns of different communities.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Implementing mechanisms for ongoing assessment and enhancement of AI governance practices.
Importance of AI Governance
Ensuring Ethical AI Use
AI governance frameworks are essential for ensuring that AI technologies are used ethically. This involves preventing harmful biases, ensuring transparency in decision-making processes, and protecting individual privacy. Ethical AI use builds trust among users and fosters public confidence in AI technologies.
Mitigating Risks and Harms
Effective AI governance helps identify and mitigate risks associated with AI, such as unintended consequences, security vulnerabilities, and misuse. By proactively addressing these risks, organizations can prevent potential harms and enhance the safety and reliability of AI systems.
Promoting Accountability
AIgovernance promotes accountability by establishing clear guidelines and standards for AI development and use. This ensures that developers, organizations, and users are held responsible for the outcomes of AI systems, encouraging more responsible and conscientious practices.
Facilitating Innovation and Adoption
A well-defined governance framework can facilitate innovation by providing clarity and guidance on the ethical and legal considerations of AI use. This can accelerate the adoption of AI technologies by reducing uncertainty and fostering a supportive regulatory environment.
Enhancing Global Cooperation
AI governance frameworks can promote global cooperation by harmonizing standards and practices across different countries and regions. This can facilitate cross-border collaboration, data sharing, and the development of global AI solutions to address common challenges.
Key Principles of AI Governance
Fairness
Fairness in AI governance involves ensuring that AI systems do not discriminate against individuals or groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, age, or socioeconomic status. This requires addressing biases in data, algorithms, and decision-making processes.
Transparency
Transparency entails providing clear and understandable information about how AI systems operate, including their decision-making processes and underlying algorithms. This helps users and stakeholders understand and trust AI technologies.
Accountability
Accountability involves establishing mechanisms for holding developers, organizations, and users responsible for the outcomes of AI systems. This includes clear guidelines for reporting, auditing, and addressing any negative impacts or misuse of AI.
Privacy
Privacy in AI governance involves protecting individuals’ personal data and ensuring that AI systems comply with data protection laws and regulations. This includes implementing robust data security measures and obtaining informed consent from users.
Safety and Security
Ensuring the safety and security of AI systems is a critical aspect of AI governance. This involves identifying and mitigating potential risks, such as security vulnerabilities, and implementing measures to prevent unintended consequences or misuse.
Inclusivity
Inclusivity entails involving diverse stakeholders in the governance process, including marginalized and underrepresented groups. This ensures that AI systems address the needs and concerns of all communities and do not perpetuate existing inequalities.
Current AI Governance Frameworks
Regulatory Approaches
European Union: The AI Act
The European Union’s AI Act is one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks for AI. It classifies AI systems into different risk categories (unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal) and establishes specific requirements for each category. The AI Act emphasizes transparency, accountability, and human oversight, aiming to ensure the ethical and safe use of AI technologies across the EU.
United States: AI Initiatives
The United States has taken a more decentralized approach to AI governance, with various initiatives and guidelines developed by different federal agencies. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has published a framework for managing AI risks, while the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) provides guidance on the ethical use of AI in consumer protection.
China: AI Regulations
China has implemented several regulations to govern the use of AI, focusing on data security, privacy, and ethical considerations. The country has also established guidelines for AI development in specific sectors, such as healthcare and autonomous vehicles. China’s approach emphasizes state control and oversight to ensure compliance with national priorities.
Industry Standards
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 42
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have established a joint technical committee (JTC 1/SC 42) focused on developing international standards for AI. These standards address various aspects of AI, including terminology, data quality, risk management, and ethical considerations.
IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has launched the Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems, which aims to ensure that AI technologies are aligned with ethical principles. The initiative has developed a series of standards and guidelines for ethical AI design, development, and deployment.
Organizational Practices
AI Ethics Committees
Many organizations have established AI ethics committees to oversee the development and use of AI technologies. These committees are responsible for ensuring that AI systems adhere to ethical principles, conducting impact assessments, and providing guidance on ethical dilemmas.
Internal AI Governance Policies
Organizations are increasingly developing internal AI governance policies to guide their AI initiatives. These policies typically include guidelines on data privacy, algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation, and accountability. Regular training and awareness programs are also implemented to ensure compliance with these policies.
Challenges in AI Governance
Balancing Innovation and Regulation
One of the primary challenges in AI governance is finding the right balance between promoting innovation and ensuring regulatory compliance. Overly restrictive regulations can stifle innovation, while insufficient regulation can lead to ethical lapses and public distrust. Policymakers must strike a balance that fosters innovation while safeguarding societal values.
Addressing Bias and Fairness
Bias in AI systems is a significant challenge that can result in unfair and discriminatory outcomes. Addressing bias requires comprehensive strategies, including diverse and representative data collection, algorithmic auditing, and ongoing monitoring. Ensuring fairness in AI systems is an ongoing effort that demands collaboration between technologists, ethicists, and policymakers.
Ensuring Transparency and Explainability
AI systems, especially those based on complex machine learning models, can be challenging to understand and explain. Ensuring transparency and explainability is critical for building trust and accountability. Developing methods for interpreting AI decisions and communicating them to stakeholders in an understandable manner is a key challenge in AI governance.
Protecting Privacy and Data Security
AI systems often rely on large amounts of personal data, raising significant privacy and data security concerns. Protecting individuals’ privacy while enabling the effective use of data for AI is a complex challenge. Robust data protection measures, informed consent mechanisms, and compliance with data protection regulations are essential components of AI governance.
Global Cooperation and Harmonization
AI technologies are developed and deployed globally, necessitating international cooperation and harmonization of governance frameworks. Differences in regulatory approaches, cultural values, and technological capabilities can pose challenges to global cooperation. Developing common standards and fostering international dialogue is crucial for addressing these challenges.
Adapting to Rapid Technological Advancements
AI technologies are evolving rapidly, making it challenging for governance frameworks to keep pace. Policymakers and organizations must adopt adaptive and flexible approaches to AI governance that can respond to new developments and emerging risks. Continuous monitoring, updating policies, and fostering innovation-friendly regulations are essential for staying ahead of technological advancements.
The Future of AI Governance
Dynamic and Adaptive Frameworks
The future of AI governance will likely involve dynamic and adaptive frameworks that can respond to the rapid pace of technological change. These frameworks will incorporate mechanisms for continuous monitoring, feedback, and improvement to address emerging risks and opportunities in AI development and deployment.
Ethical AI by Design
Incorporating ethical principles into the design and development of AI systems from the outset is a growing trend. Ethical AI by design involves embedding fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy considerations into AI systems throughout their lifecycle. This proactive approach can help prevent ethical lapses and build public trust in AI technologies.
Collaborative Governance Models
Collaborative governance models that involve diverse stakeholders, including governments, industry, academia, and civil society, will play a crucial role in shaping the future of AI governance. These models promote inclusivity, transparency, and shared responsibility, ensuring that AI systems address the needs and concerns of all communities.
AI Auditing and Certification
AI auditing and certification mechanisms will become increasingly important for ensuring compliance with ethical and regulatory standards. Independent audits and certifications can provide assurance that AI systems are developed and used responsibly, promoting accountability and trust.
Integration with Digital Governance
AI governance will increasingly be integrated with broader digital governance frameworks that address issues such as cybersecurity, data protection, and digital rights. This holistic approach will ensure that AI technologies are governed in a manner that aligns with overall digital policy objectives and societal values.
Education and Awareness
Education and awareness programs will be essential for fostering a culture of responsible AI development and use. Training for developers, policymakers, and the general public can enhance understanding of AI governance principles and promote ethical practices.
Conclusion
AI governance is a critical aspect of ensuring the ethical, safe, and responsible development and use of AI technologies. As AI continues to transform industries and societies, robust governance frameworks are essential for addressing the ethical, legal, and social challenges that arise. From regulatory approaches and industry standards to organizational practices and global cooperation, various mechanisms are being developed to navigate the complex landscape of AI governance.
The future of AI governance will involve dynamic and adaptive frameworks, ethical AI by design, collaborative governance models, AI auditing and certification, integration with digital governance, and education and awareness programs. By embracing these approaches, we can ensure that AI technologies are used in ways that promote innovation, enhance societal well-being, and uphold ethical principles.
As we move forward, it is crucial for policymakers, industry leaders, researchers, and the broader public to engage in ongoing dialogue and collaboration to shape the future of AI governance. By working together, we can navigate the challenges and opportunities of AI and create a future where AI technologies are harnessed for the greater good.